Blog
What Element is Used in Batteries?
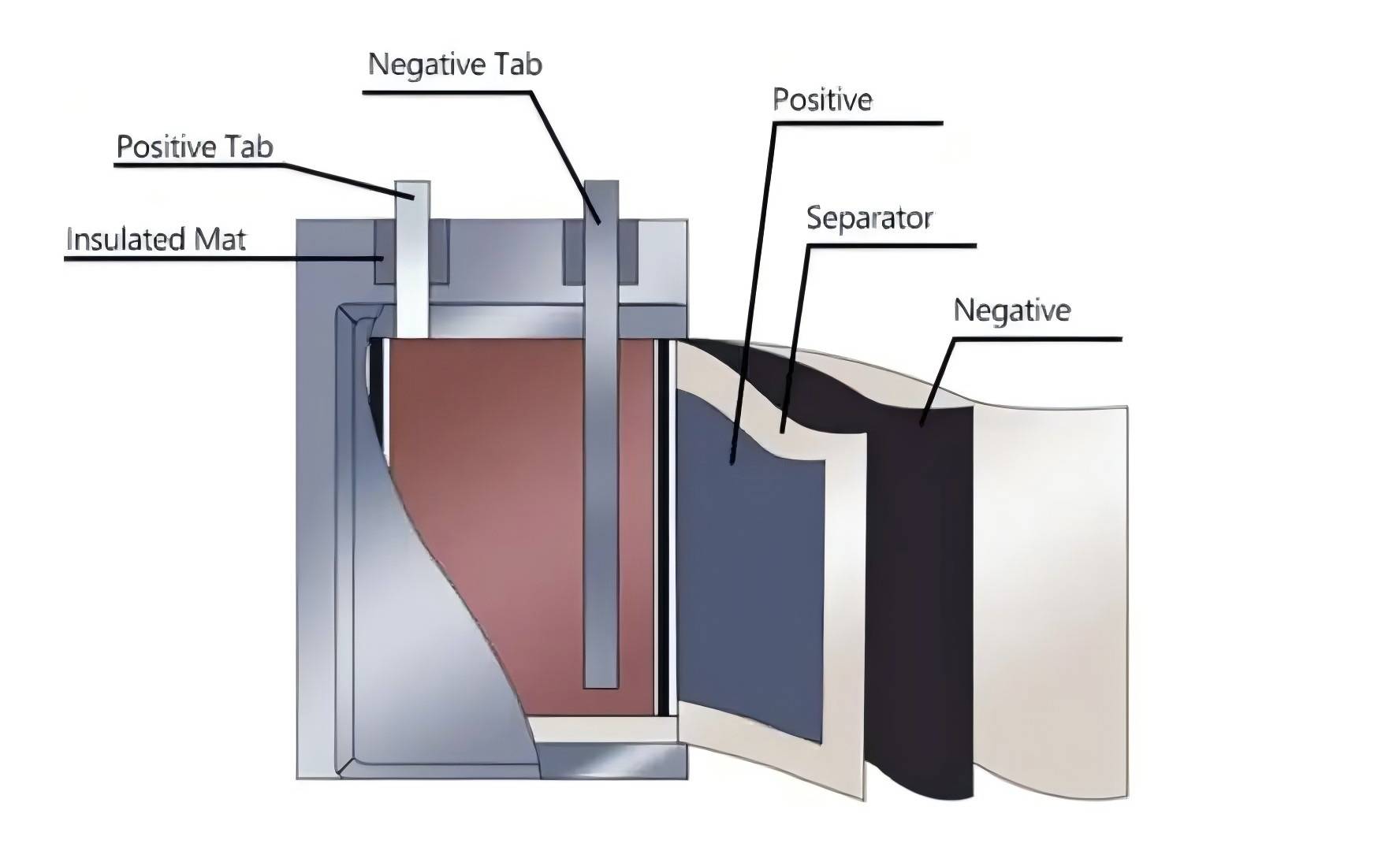
Batteries are essential to our daily lives, powering everything from smartphones and laptops to electric vehicles and renewable energy systems. But have you ever wondered what elements make up these powerful devices? In this article, we explore the key components of batteries, and break down the elements used in different battery types.
What is Inside a Battery?
Batteries consist of several critical components, each contributing to the overall functionality and performance of the device they power. These include the anode, cathode, electrolyte, and separator.
Anode Materials
The anode material is vital for conducting electricity and storing energy. It usually involves metal oxides or phosphates, which improve conductivity, stability, and compatibility.
Lithium Cobalt
Lithium cobalt was the first material used in commercial lithium-ion batteries due to its high capacity and voltage. However, it is costly and has safety concerns, so newer materials are gradually replacing it.
Lithium Manganate
Lithium manganate is a lower-cost, safer alternative that's commonly used in low-power devices and energy storage batteries. However, it suffers from capacity decay and temperature limitations.
Lithium Iron Phosphate
Known for its safety and long life cycle, lithium iron phosphate is used in high-power and energy storage batteries. However, its low capacity and poor conductivity require improvement through doping or compounding.
Ternary Materials (Nickel, Cobalt, Aluminum)
Ternary materials, such as nickel-cobalt-aluminum (NCA) and nickel-manganese-cobalt (NMC), offer high capacity and energy density. These materials are mainly used in high-power applications like electric vehicles. However, they are expensive and have a shorter cycle life compared to other options.
Carbon-based Materials
Commonly used in lithium-ion batteries, carbon-based anodes (like natural or artificial graphite) are known for their low cost, stability, and good cycling performance.
Silicon-based Anodes
Silicon anodes, known for their high capacity and energy density, are becoming popular for high-performance batteries but suffer from expansion issues during charging, which affects their durability.
Lithium Titanate Anode (LTO)
Lithium titanate offers long life and safety, making it ideal for high-power applications, but it has a lower capacity than other anode materials.
Lithium Metal Anode
Lithium metal has the highest theoretical capacity among anode materials, making it perfect for emerging technologies like lithium-sulfur and lithium-air batteries.
Separator
The separator in a battery prevents direct contact between the anode and cathode, which could lead to short-circuiting. It also allows lithium ions to pass through during charging and discharging.
Common Separator Materials
Polypropylene (PP) and polyethylene (PE) are common separator materials due to their low cost, high porosity, and stability. However, they may not offer the best thermal stability.
Organic Electrolytes
Electrolytes, typically made from lithium salts dissolved in organic solvents, enable lithium ion movement between the anode and cathode, allowing the battery to charge and discharge.
What Are the Elements in Different Batteries?
Different types of batteries use various combinations of elements. Let's look at the common battery types and their key materials.
Lithium-ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are widely used in devices like smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles due to their high energy density and long cycle life.
- Elements: The cathode typically contains lithium-based compounds like lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO₂) or lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO₄). The anode is generally made of graphite.
- Applications: These batteries are used in everything from consumer electronics to electric vehicles and large-scale energy storage systems.
Nickel-Cadmium (NiCd) Batteries
NiCd batteries are an older type of rechargeable battery that offers reliability and robustness, but they suffer from memory effect and relatively lower capacity.
- Elements: The positive electrode contains nickel oxyhydroxide (NiOOH), and the negative electrode contains cadmium (Cd). The electrolyte is typically an alkaline solution.
- Applications: Common in power tools, emergency lighting, and old mobile devices.
Lead-Acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries are widely used in automotive applications, backup power systems, and other high-current applications.
- Elements: The cathode is lead dioxide (PbO₂), the anode is sponge lead (Pb), and the electrolyte is sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄).
- Applications: Primarily used in vehicles, uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), and backup power systems.
Zinc-Carbon Batteries
- Elements: The anode is zinc (Zn), and the cathode is manganese dioxide (MnO₂). The electrolyte is typically ammonium chloride or zinc chloride.
- Applications: Widely used in devices like remote controls, flashlights, and clocks.
Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) Batteries
- Elements: The cathode is nickel oxyhydroxide (NiOOH), and the anode is a hydrogen-absorbing alloy.
- Applications: Used in everything from digital cameras to hybrid electric vehicles.
Alkaline Batteries
- Elements: The anode is zinc (Zn), the cathode is manganese dioxide (MnO₂), and the electrolyte is potassium hydroxide (KOH).
- Applications: Used in common devices like toys, remote controls, and portable radios.
Conclusion
So, what elements are used in batteries? The answer depends on the type of battery. From lithium and cobalt in lithium-ion batteries to lead and sulfur in lead-acid batteries, the materials used in battery construction determine how long they last, how quickly they charge, and how safe they are.
As battery technology advances, new materials and designs continue to emerge, making batteries more efficient and environmentally friendly. Researchers are working hard to improve existing technologies and develop even better solutions for the future.
- Next:Understanding Lithium Battery Leaks: Causes, Prevention, and Safety
- Previous:OTS LiFePO4 Batteries vs DIY LiFePO4 Batteries: Key Differences You Need to Know
Contact Details
Lithium LiFePO4 Batteries and Lithium LiFePO4 Cells Supplier - LiFePO4 Battery Shop
Contact Person: Miss. Elena Wang
WhatsApp : +8615263269227
Skype : +8615263269227
WeChat : 15263269227
Email : info@lifepo4batteryshop.com
All Products
Certification
Customer Reviews
- I have fond memories of our meeting in Shanghai with LiFePO4 Battery Shop Elena. Your company left a strong impression on me with its impressive growth and professionalism. We both value straightforwardness and honesty, which I believe are the most important qualities in any partnership. I am confident that we can build a successful collaboration based on these shared values. —— Robert from USA
- I've been working with LiFePO4 Battery Shop for years, and their reliability is unmatched. While other suppliers frequently change sales teams, LiFePO4 Battery Shop has consistently provided exceptional service with a stable team. Their commitment to quality and customer support truly sets them apart. —— Henry from Australia



